Physical Therapy for Biceps Tendinitis
Biceps tendinitis is a common cause of shoulder pain that develops due to repetitive, overhead movements that irritate and inflame the biceps tendon in the shoulder joint. Biceps tendinitis is associated with a sharp pain in the front of the shoulder that worsens when engaging in an activity requiring overhead motion. Physical therapy is an effective treatment for biceps tendinitis involving pain management, manual therapy, activity modification, postural education, and therapeutic exercise to regain strength, coordination, and range of motion in the shoulder.
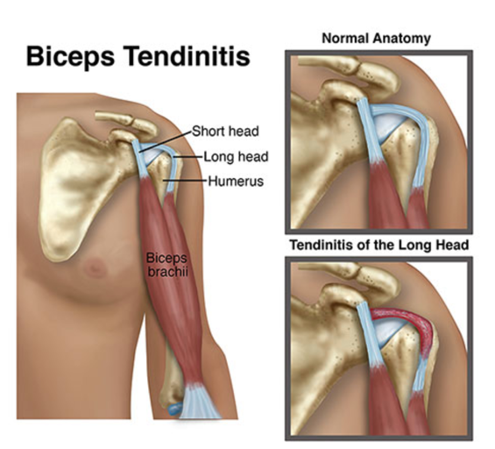
Anatomy of the Biceps Tendon
The biceps muscle is located in the front of the upper arm. The biceps tendon connects the biceps muscle in the upper arm to the elbow and to the shoulder. The biceps tendon is made up of two parts: the long and short head. The long head of the biceps tendon runs the length of the upper arm and attaches at the top of the shoulder socket to the labrum (the rim of cartilage also referred to as the glenoid), while the short head of the biceps tendon attaches to the shoulder blade.
The tendon is comprised of strands of collagen that allow the tendon to withstand forces that pull both ends of the tendon. When you move your shoulder and arm overhead, your biceps muscle pulls one end of the tendon, while the other end of the tendon pulls on the bone causing the arm and shoulder to move.
What is Biceps Tendinitis?
Biceps tendinitis is a common cause of shoulder pain and shoulder impingement that can develop over time from repetitive, overhead movements or from a traumatic accident. In biceps tendinitis, the biceps tendon (most often the long head of the tendon) becomes inflamed. In the early stages of biceps tendinitis, the tendon becomes red and swollen. As the tendinitis progresses, the sheath of the tendon thickens and grows larger. In the later stages, the tendon becomes dark red due to severe inflammation and can tear, resulting in a bulge in the upper arm.
Symptoms of biceps tendinitis include:
Sharp pain in the front of the shoulder when reaching overhead, behind the back, across the body, or when throwing
Tenderness to touch at the front of the shoulder
Pain radiating toward the neck or down the front of the arm
Dull ache of pain at front of the shoulder after an activity
Weakness felt around the shoulder joint, particularly when lifting objects or reaching overhead
Decreased range of motion in the shoulder joint
Visible change in shape and appearance of the front of the arm
Sensation of catching or clicking in front of the shoulder with movement
Difficulty in daily activities, e.g. reaching behind the back to tuck in shirt or put dishes away in an overhead cabinet
Pain when resting that becomes worse at night
Causes of biceps tendinitis involve:
Repetitive overhead activity, such as weightlifting, work activity, or sports activities (tennis, swimming, and baseball)
Improper support and weakness of the rotator cuff muscles and upper back muscles
Shoulder joint looseness (hypermobility)
Poor posture and body mechanics
Abrupt increase in volume and intensity of exercise routine
Trauma to shoulder due to a fall
Gradual development from daily wear and tear and aging process
Biceps tendinitis is common with other shoulder issues, including rotator cuff tear, shoulder arthritis, tears in the labrum, chronic shoulder instability, and shoulder impingement.
Physical Therapy Treatment for Biceps Tendinitis
Physical therapy is an effective treatment for biceps tendinitis to manage pain and restore range of motion, mobility, and strength to the shoulder joint and biceps tendon. Initially, the physical therapist completes a comprehensive physical exam of the shoulder and upper trunk. The physical therapist assesses strength, range of motion, and mobility of the shoulder; evaluates activities that ease or aggravate symptoms and arm and shoulder movement; and palpates the tender area. Based on the assessment, the physical therapist designs a customized rehabilitation program based on the patient’s specific condition.
Physical therapy treatment for biceps tendinitis involves:
Manual therapy on the shoulder, biceps muscle, and neck to mobilize the joint, muscles, and soft tissues to improve mobility and range of motion
Stretching and strengthening exercises to regain range of motion, strength, and coordination in the shoulder. Passive stretching and strengthening exercises are progressed to active exercises. This passive to active progression is critical to prevent frozen shoulder, which occurs when tissues in the shoulder shorten and tighten up, preventing full range of motion.
Strengthening exercises targeting the rotator cuff muscles and biceps muscle to relieve pressure on the biceps tendon
Functional training and simulation of daily tasks, work activities, and sports-specific actions
Education on proper shoulder position and posture, as rounded shoulders can contribute to shoulder impingement and pressure on the biceps tendon
Biceps tendinitis can cause debilitating shoulder pain and severely limit your ability to do daily tasks or engage in work and sports activities. Work with a physical therapist to relieve pain, restore shoulder mobility and range of motion, and return to sport and work safely.